Utilizing blockchain to record healthcare data can enhance the security, privacy, transparency, and ease of sharing data. Below is a detailed explanation, including the principles of how blockchain is applied in the healthcare sector.
Basic Concepts of Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that can be used to record and track healthcare data such as medical records, diagnoses, treatment plans, and prescriptions. With its decentralized, tamper-proof, and encrypted security features, blockchain brings new possibilities for healthcare data management.
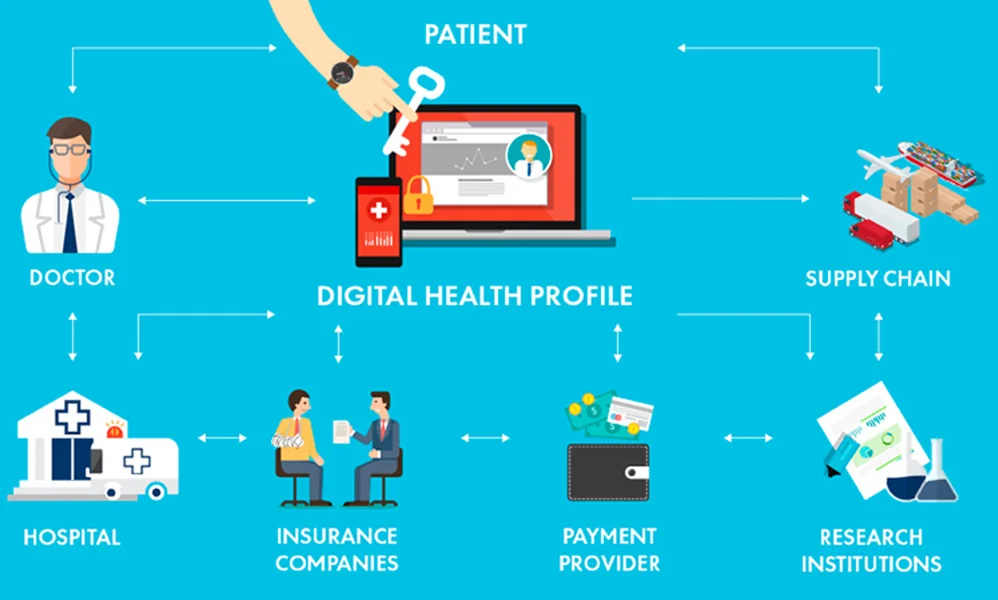
The Principles of Blockchain in Healthcare Data Recording
Decentralized Healthcare Data Storage:
Healthcare data is often centrally managed by hospitals, clinics, or health management institutions, making it vulnerable to single points of failure or external attacks. Blockchain decentralizes data, with all nodes (medical institutions, patients, etc.) holding identical copies of the ledger, eliminating the risks of centralized storage.
Medical records, test reports, and other information can be stored in a distributed manner on the blockchain, or indexed on-chain with actual data managed off-chain to handle large volumes of data.
Data Immutability:
Once healthcare data is written into the blockchain, it cannot be altered. This is crucial in healthcare, as it prevents malicious data modification or deletion, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of medical records.
For instance, once a patient's diagnosis or treatment record is recorded on the blockchain, a unique hash is generated, and any modifications will be reflected across the entire chain, ensuring that all nodes are synchronized.
Data Encryption and Privacy Protection:
Healthcare data typically contains highly sensitive personal information, making privacy protection critical. Blockchain uses public and private key encryption to safeguard data privacy.
Only the patient or authorized medical institutions can access or decrypt the data using a private key, while a public key can be used for identity verification and transaction confirmation, ensuring secure data transmission.
Additionally, blockchain can use advanced technologies like zero-knowledge proof, allowing data verification without revealing the actual data. For example, proving a patient meets specific medical conditions without disclosing their detailed medical records.
Automated Data Management with Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts are automated programs running on the blockchain that can execute automatically based on predefined conditions. They can manage healthcare data access permissions.
For example, a patient can set rules via a smart contract, allowing only specific doctors or institutions to access their medical records under certain conditions (such as emergencies). This gives patients autonomy over their data.
Data Traceability and Transparency:
Blockchain-recorded healthcare data is transparent, with all access, modification, or sharing activities logged and stored on the blockchain, making them traceable and auditable.
This is especially important for managing the pharmaceutical supply chain. For example, each stage of drug production, transportation, and sales can be recorded on the blockchain, preventing counterfeit drugs from circulating and ensuring traceability.
Workflow of Blockchain in Healthcare Data Recording
Patient Data Generation and Encryption:
When patients undergo medical examinations or treatments, the generated records and lab results are encrypted and assigned a unique identifier (e.g., hash) that is recorded on the blockchain.
Actual medical data can be stored in off-chain databases, with the blockchain storing the data index and encryption proof, ensuring data integrity.
Data Access Permission Management:
Patients and healthcare institutions use public and private keys to manage data access permissions. Patients can authorize doctors to access specific health data using their private key, and doctors verify their identity with the public key, ensuring only authorized personnel can access the data.
Smart contracts can also assist in automating this permission distribution, making patient control over data more flexible and granular.
Data Sharing and Auditing:
If patients need to share data with other hospitals or doctors, they can authorize access via the blockchain. All access operations are logged on the blockchain for audit purposes.
This sharing mechanism avoids information silos between different healthcare institutions, ensuring patients receive continuous care across locations or systems.
Data Security and Privacy Protection:
Blockchain uses encryption and distributed storage to ensure data security, while technologies like zero-knowledge proof can protect privacy without compromising data.
Only authorized users can decrypt and view healthcare data. Unauthorized users cannot read the data even if they obtain it.
Advantages of Blockchain in Healthcare Data Recording
Data Security and Privacy Protection:
By using encryption and decentralized storage, blockchain effectively prevents data leaks, tampering, or loss, ensuring the safety and privacy of patients' personal health data.
Data Sharing and Interoperability:
Blockchain enables data exchange between different hospitals, healthcare systems, and insurance companies, improving healthcare efficiency. For example, patient records can be easily transferred between hospitals without the need to re-collect data.
Patient Control Over Data:
Blockchain gives patients full control over their health data, allowing them to selectively share it, with only authorized medical institutions having access.
Lower Operational Costs and Increased Efficiency:
With blockchain, healthcare institutions can streamline processes, reduce intermediary steps in data verification, sharing, and management, thus lowering operational costs and increasing the efficiency of healthcare services.
Challenges in Blockchain Healthcare Data Recording
Data Storage and Performance Issues:
Healthcare data is often large, especially image data such as X-rays or MRI scans. Storing such large data volumes on the blockchain is impractical, necessitating off-chain storage solutions that add complexity.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues:
Different countries and regions have different regulations for managing healthcare data, such as GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the U.S. Blockchain technology must carefully address these compliance requirements.
Private Key Management:
Patients need to safeguard their private keys, as losing them means losing control over their healthcare data. Designing a secure private key recovery mechanism is one of the challenges faced by current blockchain systems.
Adoption and Cost:
While blockchain technology holds great potential, its adoption by healthcare institutions may require extensive system upgrades and technical training, leading to high initial costs.
Real-World Applications
MedRec: MedRec is a blockchain-based medical record system developed by MIT, aimed at providing patients with comprehensive health record management services through blockchain. It decentralizes patient records and enables data sharing across healthcare institutions.
PharmaLedger: This is a blockchain project for pharmaceutical supply chain management, recording the entire process of drug production, distribution, and delivery to ensure transparency and reliability of drug sources.
BurstIQ: BurstIQ is a blockchain platform focused on the secure storage and sharing of healthcare data. It uses blockchain technology to help patients, doctors, and researchers better manage and share health data.
FAQ
Q: How does blockchain handle the scalability of healthcare data?
A: Blockchain can handle large-scale data through off-chain storage solutions. For example, complex data such as large images can be stored in traditional databases, while only the data index and cryptographic proof are stored on the blockchain. This method ensures data integrity and security while efficiently managing large volumes of data.
Q: How does blockchain achieve interoperability between different healthcare systems?
A: Blockchain creates a shared decentralized ledger, allowing all participants to access the same data records. Each hospital or healthcare institution can interact with the blockchain through standardized interfaces, enabling seamless data sharing. This mechanism eliminates information silos and ensures that patients receive continuous care across different healthcare systems.
Q: How is the security of smart contracts ensured?
A: The security of smart contracts can be enhanced through code audits and the use of verified smart contract templates. Transparent open-source code allows other developers to review the contract's security. Additionally, the immutability of the blockchain ensures that once a contract is deployed, it cannot be tampered with, providing security during execution.
Q: How can patients ensure the security of their data?
A: Patients can secure their data by properly managing their private keys, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access their health information. Patients can also enhance security through multi-factor authentication and regularly updating access permissions. Educating patients on the safe use of blockchain technology is also crucial.
Q: How are different countries' laws and regulations regarding healthcare data managed?
A: Blockchain projects need to work closely with legal advisors and compliance experts to ensure adherence to each country’s laws. This can be achieved by creating smart contracts and data storage mechanisms that comply with specific regulations. For instance, data might need to be stored locally to comply with data protection laws like GDPR.
Related Articles

What is SparkLend? A Beginner-to-Advanced Guide to Decentralized Lending Made Easy
SparkLend is a decentralized, non-custodial liquidity market protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain. Simply put, it functions like a bank without intermediaries, allowing users to borrow and lend d
June 26, 2025
What is sUSDS? How Do I Acquire sUSDS?
This guide will walk you through Sky Savings’ sUSDS and sUSDC—your gateway to earning yield with stablecoins while keeping your funds secure.Sky Savings: Your Journey to Stablecoin Yields Begins HereW
June 26, 2025
What is SparkLend? A Complete Guide from Beginner to Pro
SparkLend is a decentralized, non-custodial liquidity market protocol that allows users to participate as lenders or borrowers. Lenders provide liquidity to earn passive income, while borrowers can ta
June 24, 2025
What Exactly Does Spark Protocol Do? A Complete Guide
This guide will walk you through Spark Protocol — an innovative platform designed to tackle the long-standing issue of fragmented liquidity in the DeFi space. You'll learn how to earn yield, borrow as
June 24, 2025
RXS Token Trading Guide: From Presale to Uniswap – A Complete Walkthrough
This guide will walk you through the trading process of the RXS Token, from the restrictions during the presale phase to free trading on Uniswap, helping you trade securely and efficiently.1. Introduc
June 24, 2025
